What Is Skin Biopsy?
Skin biopsy is an important diagnostic procedure that is routinely performed in dermatological practice. Although the technique is simple, the choice of the type and location of the sample is essential to obtain a useful portion.
Through the realization of it , a close-up and specific view of the situation of the fabric is accessed. Therein lies its importance, since many other diagnostic procedures are more superficial and do not allow the intimacy of results that a skin biopsy does have.
What is a skin biopsy and what is it for?
Skin biopsy is indicated to diagnose dermatological conditions and sometimes for systemic diseases that have skin or soft tissue manifestations. This could be the case with rheumatoid arthritis, for example.
In addition, the accuracy of the diagnosis can be improved through the use of dermoscopy when selecting the biopsy site. Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence staining techniques are applied when appropriate and precision is improved, according to studies by Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia .
You may be interested: Benign skin tumors: how do they manifest themselves?
Different types of skin biopsy
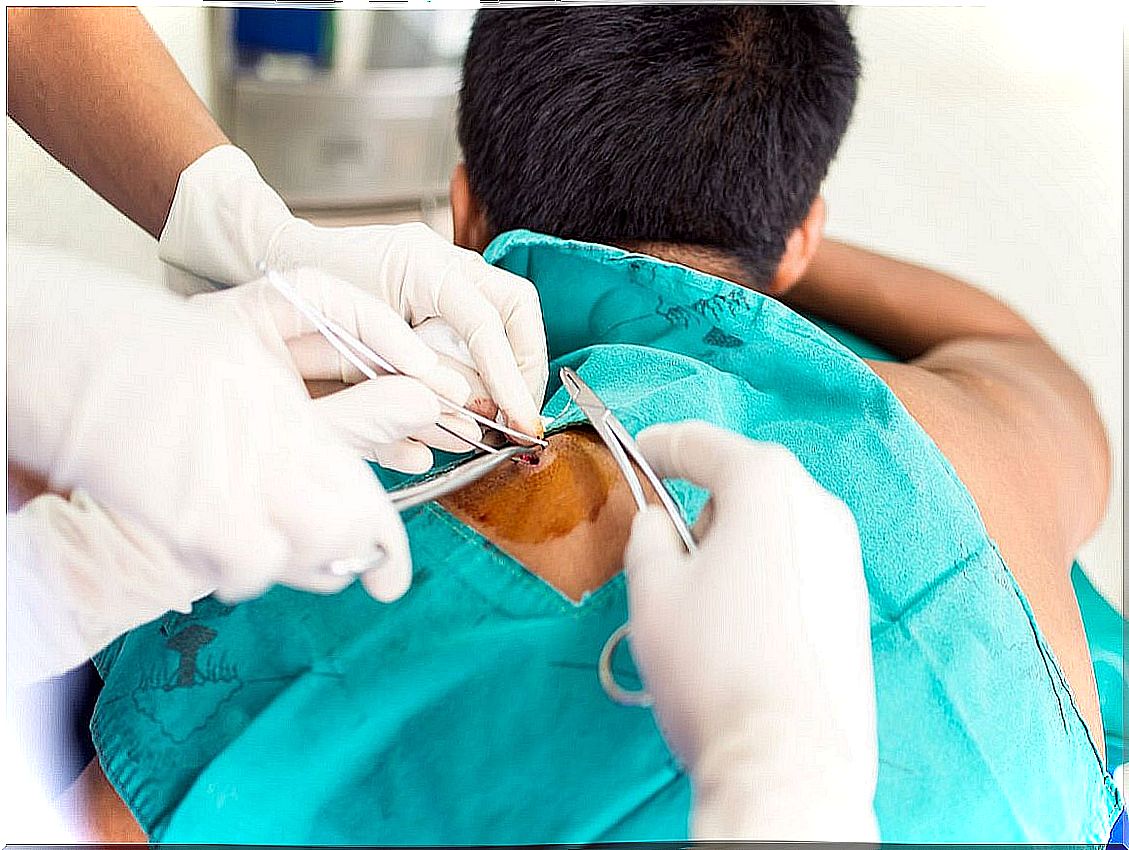
There are several methods of skin biopsy and multiple factors are considered when choosing the most appropriate technique for a given situation. Generally speaking, they can be classified as incisional (only a sample is taken from part of an injury) or excisional (in which the doctor removes all of the visible injury).
Shave biopsy
Scrap skin biopsy uses a scalpel or hand blade to take a sample of the desired thickness. This method is best for superficial processes or for diagnosing non-melanoma skin cancers, according to studies by FP Essentials.
The area is cleaned first and the area is numbed. The skin is then stretched with the non-dominant hand while using the scalpel to obtain the tissue sample.
In punch
Punch biopsy is another incision method that uses a cylindrical blade to obtain a sample that contains a fuller thickness of the skin. Because it provides greater depth, this variant is often the best option for diagnosing inflammatory conditions.
The punches are available in various diameters and the most commonly used sizes range from 2 millimeters to 6 millimeters. In particular on the face, you can choose one of the smallest. When performing this biopsy, the punch must be rotated while applying pressure to the skin.
Excisional
This type of technique consists of completely and deeply eliminating the entire lesion, down to the subcutaneous plane. The wound can be closed mainly with sutures. This method is preferred when a neoplasm is suspected.
What should be the preparation and what possible risks are there in a skin biopsy?
Before performing the procedure, the patient should inform the doctor if he or she suffers from the following conditions:
- You are under anticoagulant treatment: take aspirin, warfarin, clopidogrel or other antiplatelet drugs.
- You have a bleeding disorder: a diathesis or Von Willebrand syndrome, for example.
- He is immundepressed: because he is being treated with medication that depresses the immune system or suffers from a chronic condition in this sense.
- Allergies
Apart from this, the skin biopsy does not involve any special preparation by the patient. There are usually no contraindications or risks after the moment of carrying out this type of technique. However, some of the complications that are often mentioned are the following:
- Bleeding at the biopsy site.
- Hematoma.
- Wound infection
- Poor healing
Pressure bandages and ice can minimize the development of bleeding or bruising. A posterior suture is often required, particularly after a needle biopsy greater than 4 millimeters.
Post-skin biopsy care
This approach is outpatient, which means that the patient is immediately removed home. Therefore, a bandage is placed over the area, which may be tender for a few days afterward. There may be a small amount of bleeding, not significant.
The goal is to keep the area clean and dry. Care should be taken not to hit or stretch the skin near the area where the sample was taken, which can cause increased bleeding. If stitches were done, they will be removed in about 7 to 10 days.
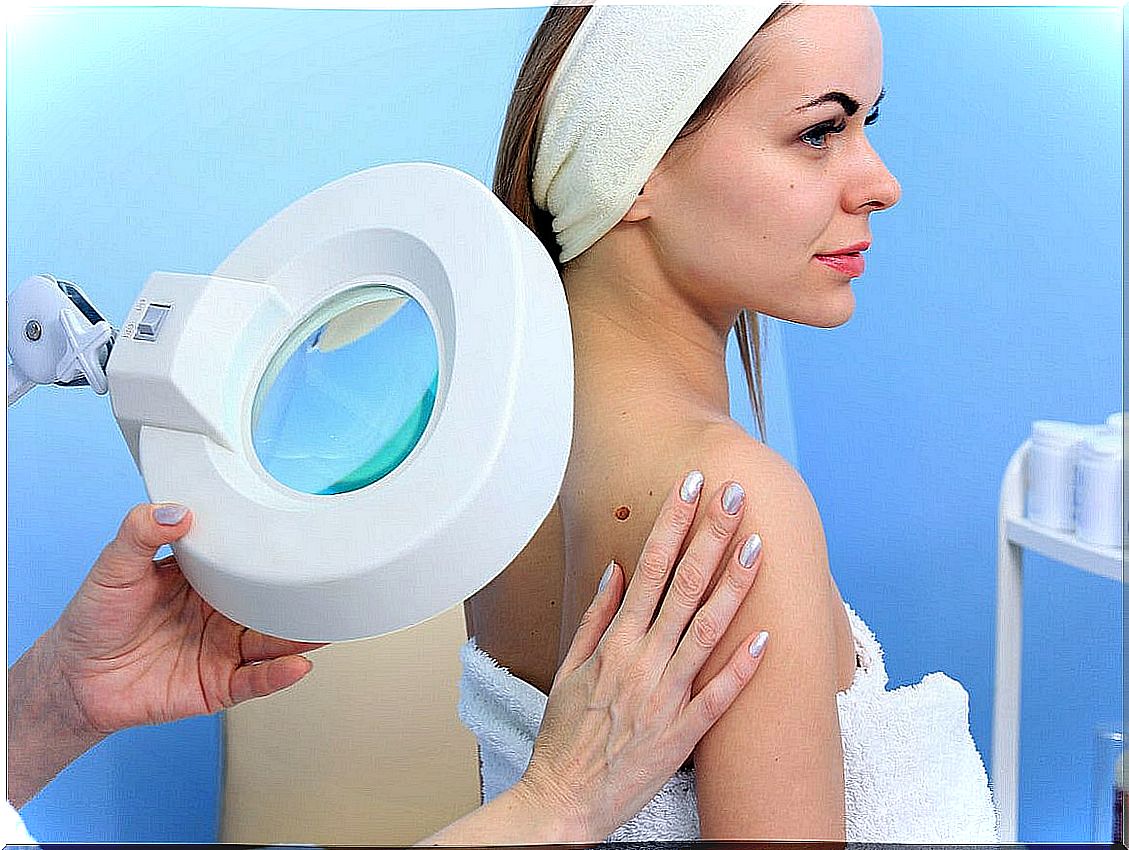
What can be the results?
The tissue that was removed is sent to a pathology department and examined under a microscope. Most of the time, results are returned within a few days, at most a week later.
If a skin lesion is benign, you may not need any additional treatment. If the entire skin lesion was not removed at the time of the biopsy, the doctor will indicate to remove it completely in a second therapeutic instance.
Some of the skin pathologies that can be diagnosed with skin biopsy are the following:
- Melanoma.
- Squamous cell carcinoma.
- Basal cell carcinoma.
- Inflammatory psoriasis or dermatitis.
- Fungal or bacterial infections
Read also: Treatment of skin cancer (melanoma)
An effective and safe procedure
Due to the low risk, a skin biopsy can be performed safely and routinely in a hospital or outpatient setting. There are no major complications and recovery is immediate.
Skin biopsies are used to help confirm a diagnosis. The intention is to characterize the nature of a skin growth or rash to aid in the evaluation of the clinical picture. In this way, the doctor can have more elements to begin the correct approach.