Trench Mouth: Origin, Symptoms And Treatment
Trench mouth, also known as acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis or GUNA, is a very rare disease today. The characteristic nickname comes from the fact that it used to affect war soldiers, due to the unhealthy conditions and habits that arose during conflicts.
It presents in the form of an acute and painful infection in which the gums bleed, with a necrosis of the papillae and an attack on the general oral condition. According to studies, it is currently linked to AIDS, since acquired immunodeficiency usually causes oral pathologies in 90% of these patients.
What causes it?
Trench mouth is a painful form of gum inflammation, something known as gingivitis . The bacterial species Bacillus fusiformis and Borrelia Vincentii are associated with the lesions presented here, although they are not the only ones.
As scientific studies indicate, 4 areas are differentiated in the affected region:
- Bacterial: composed of a large mass of bacteria with different morphologies and characteristics. These do not have to be harmful in the first instance, since it is their excessive proliferation that causes the disease.
- Rich in neutrophils: Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes in the blood and one of the first to reach infectious foci. They are part of the pus and appear, in this case, under the bacterial region.
- Necrotic: it is the place where cell death occurs. Here the spirochetes, a type of bacteria with an elongated and helical shape, dominate.
- Spirochetal infiltration: the last layer, in which the spirochetes infiltrate and other types of bacteria are not observed.
According to the United States National Library of Medicine, trench mouth bacterial overgrowth can be triggered by the following factors: stress, poor oral hygiene, smoking, malnutrition, and a weak immune system.
What are the symptoms of trench mouth?
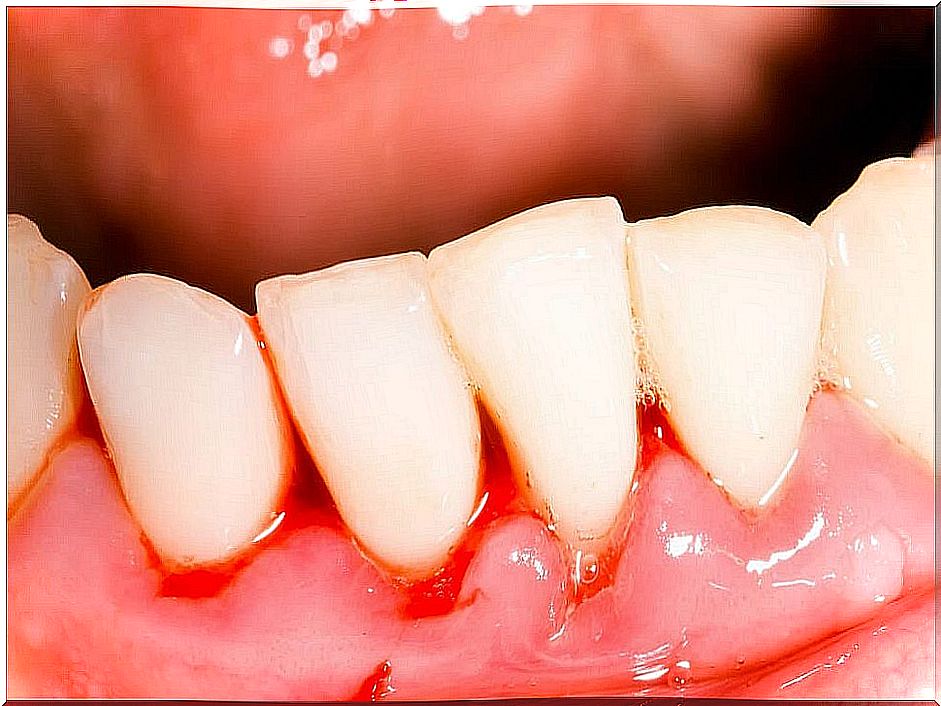
The MSD manual indicates that the infection usually begins suddenly, with pain and bleeding in the gums plus excessive salivation. Some of the most common clinical signs are:
- Bad breath, conspicuous by its unpleasant smell.
- Crater-like ulcers between the teeth.
- Fever.
- Unpleasant taste in the mouth, perceptible by the patient himself. Some describe it as a metallic taste.
- Grayish films on the gums, which appear red and bloody.
Due to all these symptoms, the patient will have difficulty performing common activities, such as speaking, eating, and swallowing. The lymph nodes in the neck are also often swollen in response to infection (lymphadenopathy).
Possible complications
When presenting difficulties to eat and lead a normal life, some common complications are that the patient loses weight, suffers from dehydration and begins to lose teeth. If all of these clinical signs are ignored, it is possible for bacteria to infiltrate the blood, in an event known as bacteremia .
A spread of the infection can be devastating. Multiple organs are affected and, in addition, the appearance of septic shock is favored , in which the body overreacts and a drop in blood pressure occurs.
How is it diagnosed?
As indicated by the scientific portal Drugs , the physical examination is the first step to detect a trench mouth. The professional will look for ulcers, grayish plaques around the teeth, and destruction of the gum tissue. Suspicion is usually quick and the diagnosis leaves little room for error.
If there are doubts, you can go for blood tests and X-rays. The latter are used to assess the amount of damage produced by the infection, since the extent of the lesions can be clearly observed. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, multiple approaches are followed.
When to seek medical help?
Before any type of inflammation in the gums it is necessary to go to the doctor. Not all of them happen due to infections, but it is necessary to rule out pathologies and never let time pass.
An oral infection can be greatly aggravated if it is not addressed in time, since bacteria have the ability to pass into the bloodstream.
Treatments available for trench mouth
According to the Siegfried Rhein health portal, the goals of treatment are to cure the infection and relieve symptomatological discomfort. This can be achieved through the use of antibiotics, although the fundamental pillars for the trench mouth are the following:
- Professional cleaning: performed at the dentist slowly and thoroughly over several consecutive days. The disease usually responds very well to oral hygiene.
- Mouth rinses : the patient at home should perform periodic rinses with salt water or a hydrogen peroxide solution.
- Good oral hygiene: during the first days the patient is usually advised not to brush their teeth, due to the fragility of the oral apparatus due to the disorder. After rinsing and cleaning, it is necessary to brush your mouth for the rest of your life to prevent its reappearance.
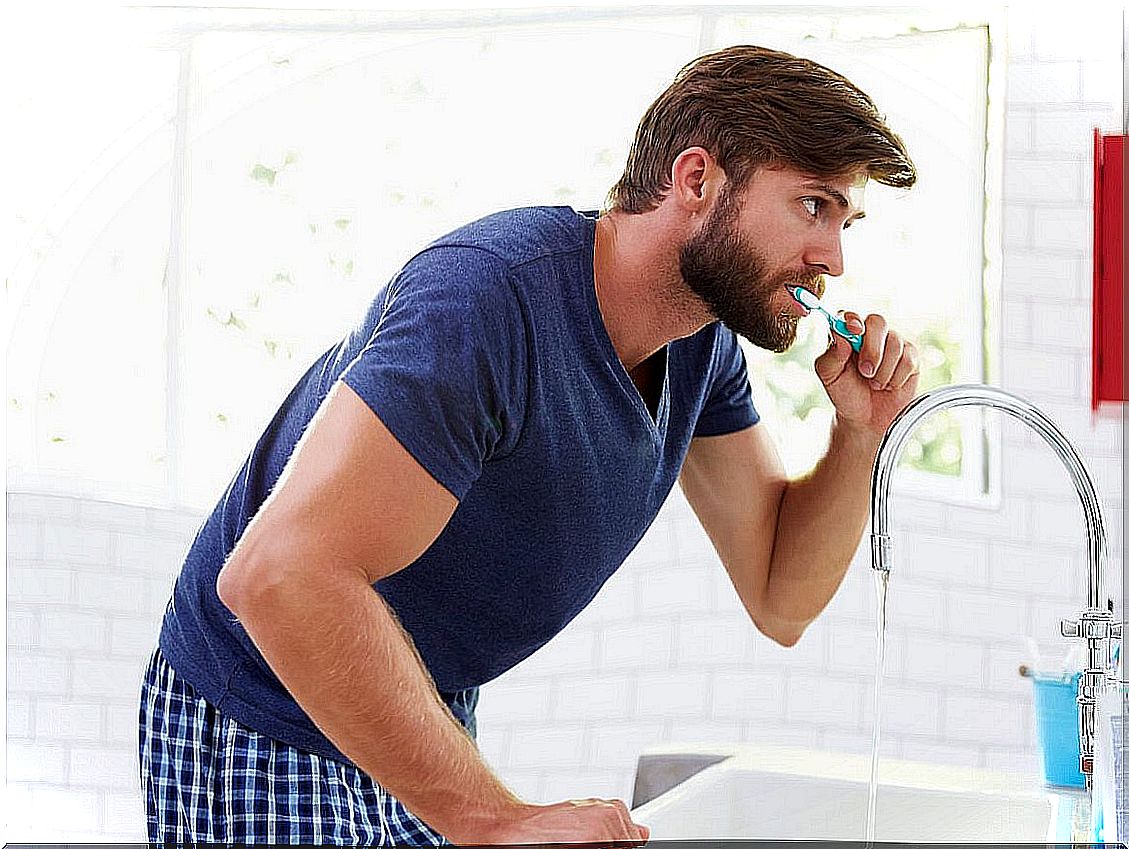

Prevention
Prevention is clear and is based on good nutrition, correct oral hygiene and going to the dentist from time to time for check-ups. Patients are also advised, in all cases, to start exercising and stop smoking.
In addition to all this, the trench mouth has an important psychological component, since in many cases it is related to stress. Therefore, sometimes it is necessary to seek help beyond the pharmacological field to address pathologies like this.
The trench mouth has almost disappeared
Trench mouth is an increasingly rare disease, as standards of personal hygiene increase more and more. To avoid its appearance, it is necessary to brush your teeth every day and visit the dentist periodically in order for him to evaluate possible imbalances.