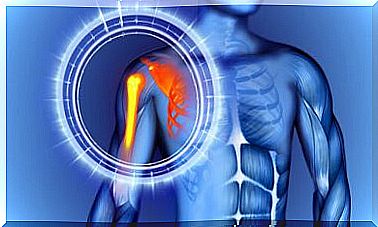
Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint is complex since it is made up of several joints. All of them work together to allow a global harmonic movement. If any fail, the movement of the shoulder will be affected.
Today we want to explain how this complex part of the body works, but it is so necessary to make countless daily movements.
Shoulders
The shoulders are the anatomical region that joins the arms with the trunk. In turn, this region is composed of the union of three bones: shoulder blade, clavicle and humerus. Their special arrangement is what gives rise to various joints.
The shoulder joint acquires stability thanks to the muscles. These are responsible, in the first place, to allow movement. In addition, they provide support to the joint.
Much of the daily movements, especially those performed above the head, depend on the shoulders.
The shoulder joint: a complex apparatus
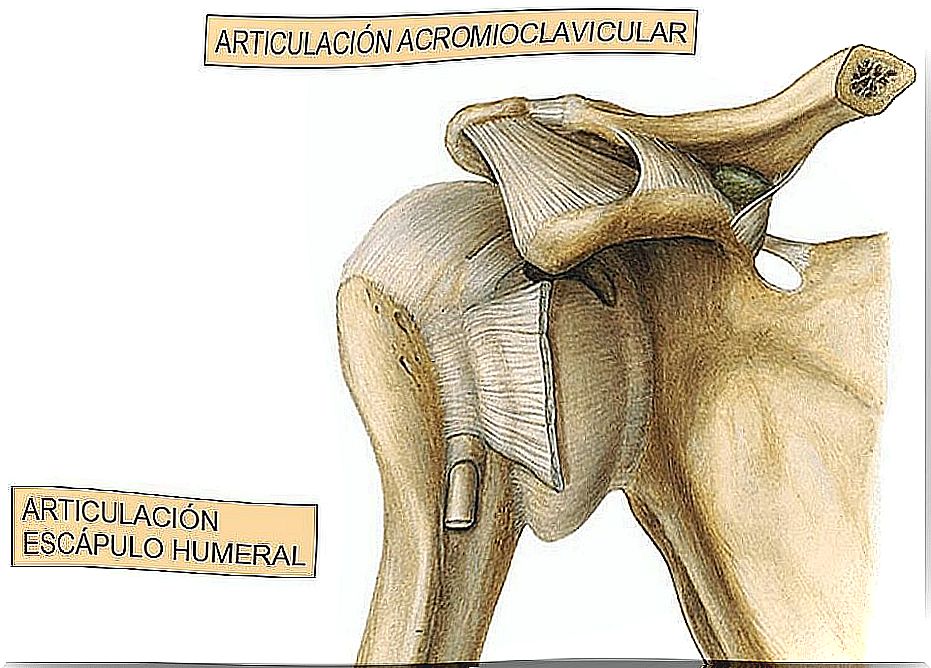
The shoulder joint is a joint complex. The joints that compose it are divided into two basic groups.
First group
- Glenohumeral joint. It is made up of the head of the humerus and the glenoid cavity. It is the most important of all.
- Subdeltoid joint. It is considered a joint from a physiological point of view, but not an anatomical one. In it, there are two surfaces that glide past each other: the deep face of the deltoid and the rotator cuff. It also includes a serous bag, which facilitates movement. This joint is attached to the glenohumeral. Thus, a movement in the glenohumeral also generates movement in the subdeltoid.
Second group
- Scapulothoracic joint. In it the scapula slides over the rib cage. It is also considered a physiological joint, but not an anatomical one. It is the most important of this group. It is mechanically linked to the other two.
- Acromioclavicular joint. It is located in the external segment of the clavicle.
- Sternoclavicular joint. It is located between the inner portion of the clavicle and the upper part of the breastbone.
The ligaments of the shoulder joint
The union between the arms and the trunk is possible thanks to several groups of ligaments:
- Capsular ligament. It goes from the neck of the humerus to the glenoid cavity. It is fibrous and cuff-shaped.
- Coracohumeral ligament. It is inserted between the scapula and the humerus. It is thick and resistant.
- Glenohumeral ligaments. There are three: upper, middle and lower. They run through the entire humerus.
- Transverse humeral ligament.
- Coracoglenoid ligaments.
Scapulohumeral movements and rhythm
The movements of the shoulder joint are carried out on the basis of three axes:
- The transversal, which directs flexion-extension movements.
- The anteroposterior, which directs abduction-adduction movements.
- The vertical, which directs the rotational movements.
- Likewise, all of them produce a fourth movement: that of circumduction.
Shoulder movements give rise to two important functions : scapulohumeral (SH) rhythm and stability of the shoulder complex. The scapulohumeral rhythm is a combination of the movement of the scapulothoracic and glenohumeral joints. Their functions are:
- Distribute movement between the two joints to expand their range.
- Facilitate joint congruence, that is, harmony between the different components.
- Help the muscles act on the humerus.
Shoulder stability
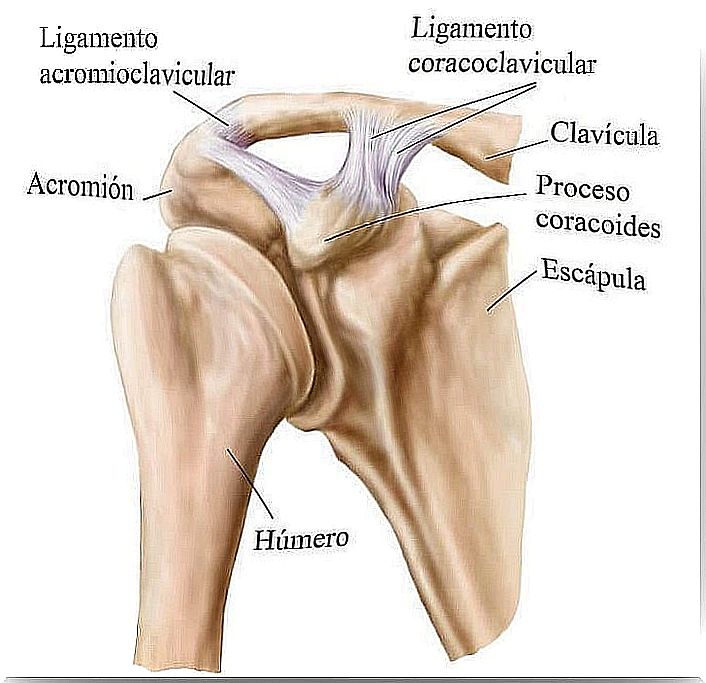
On the other hand, the stability of the shoulder is guaranteed by a complex interaction. It involved static stabilizing elements, ie the articular surfaces of the humerus and the glenoid labrum glenoid, the capsule and ligaments.
Dynamic stabilizing elements are also involved. These are the glenohumeral muscles, the scapulo-thoracic muscles, and the thoracohumeral muscles. Also, the rotator cuff is the stabilizing element.
For its part, the long biceps tendon complements this function. Finally, the synovial fluid acts as a passive limiter of movement.
The shoulder joint is the one with the greatest mobility within the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, it is subject to multiple injuries and ailments. In fact, it is the one that dislocates the most easily. Therefore, it is important to pay special attention to it.