First Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis In The Hands
Osteoarthritis is a disease that affects the cartilage of a joint, destroying them little by little. It is a chronic pathology, that is, the subject in question presents it for the rest of his life. Osteoarthritis in the hands is one of the most common, along with the spine, knees and hips.
We can differentiate two types of osteoarthritis: primary (without a specific cause) and secondary (with a specific trigger).
Among the most common triggers we find congenital diseases, injuries or trauma or other disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Also performing a repetitive activity (during work or practicing a sport) can wear down the cartilage that involves this action.
As a general rule, it appears more frequently in women and in people over the age of sixty-five. We can also point to other risk factors or conditions that increase the chances of presenting the disorder. For example, being overweight or obese, menopause, trauma and having a history (a family member who has suffered from the disease).
Symptoms of osteoarthritis in the hands: pain and more
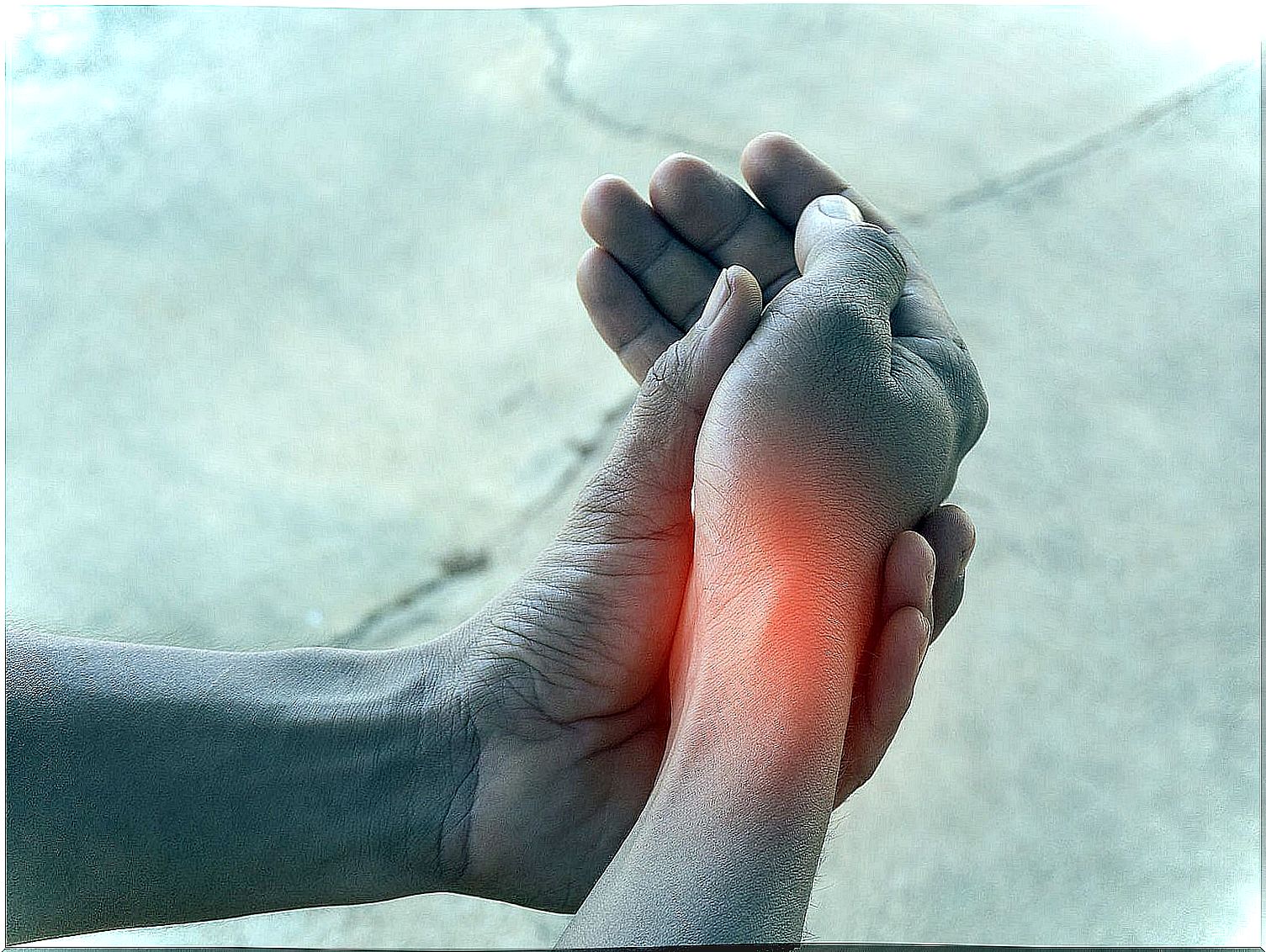
At the beginning or in the early stages of this pathology, the patient usually presents certain signs or symptoms. Among the most common we can find the following:
- Inflammation of the affected joint.
- Presence of edema (an accumulation of fluid) in the nearby regions.
- Cracking or noises when making a movement with the hands after a period of rest.
- Stiffness or numbness of the limbs altered after a period of inactivity. It is also common to feel tingling at different times during the day.
- Difficulty carrying out any movement that involves this joint, especially after a few moments of rest.
- Formations lumps or bumps on the skin of the hands (they are also called subcutaneous nodules). Therefore, these nodules cause the deformation or the unsightly appearance.
- Pain or discomfort that can vary in intensity. There are certain clinical cases in which the patient does not present this discomfort. It is caused by friction between the bones that make up the joint. In this way, the cartilage does not fulfill its usual functions.
The diagnosis of this disease can be made through a physical examination (especially the deformations are analyzed) together with other medical procedures.
As a general rule, they include both the analysis of substances (mainly blood, urine and synovial fluid) and the obtaining of images (X-rays, ultrasound of the joints, MRI, etc.).
Treatment of osteoarthritis in the hands
The treatment of osteoarthritis in the hands is personalized and depends on the degree of evolution of the disease. Some general measures include various medications that relieve the patient’s pain or inflammation of the affected joints, in this sense we speak of analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs as classic symptomatic treatment.
But that’s not all, in recent years other drugs that modify the course of the disease have been progressively introduced , that is, although they do not cure osteoarthritis, they slow its progress.
In this way, the patient remains mobile for longer and is self-sufficient for daily tasks. Within this family of innovative drugs, chondroprotectors stand out, such as chondroitin sulfate, which is found naturally in the cells that surround the extracellular matrix in the body.
Prevention
The corresponding doctor can recommend a series of guidelines, in order to alleviate the symptoms and delay the progression of the disease. For example, the use of certain drugs to reduce inflammation (anti-inflammatories) and discomfort (analgesics) that the patient may suffer. Also, in more advanced cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pain.
On the other hand, there are numerous recommendations that do not involve medical treatment. We include exercising, both to maintain a healthy quality of life and to avoid being overweight. Also the use of splints and avoid certain activities to avoid overload.
Finally, patients can apply heat to loosen the disturbed region and cool to reduce swelling or inflammation.