Coronary Angioplasty
This procedure is often combined with permanent placement of a small wire mesh tube that is intended to reduce the chance of a new obstruction or narrowing.
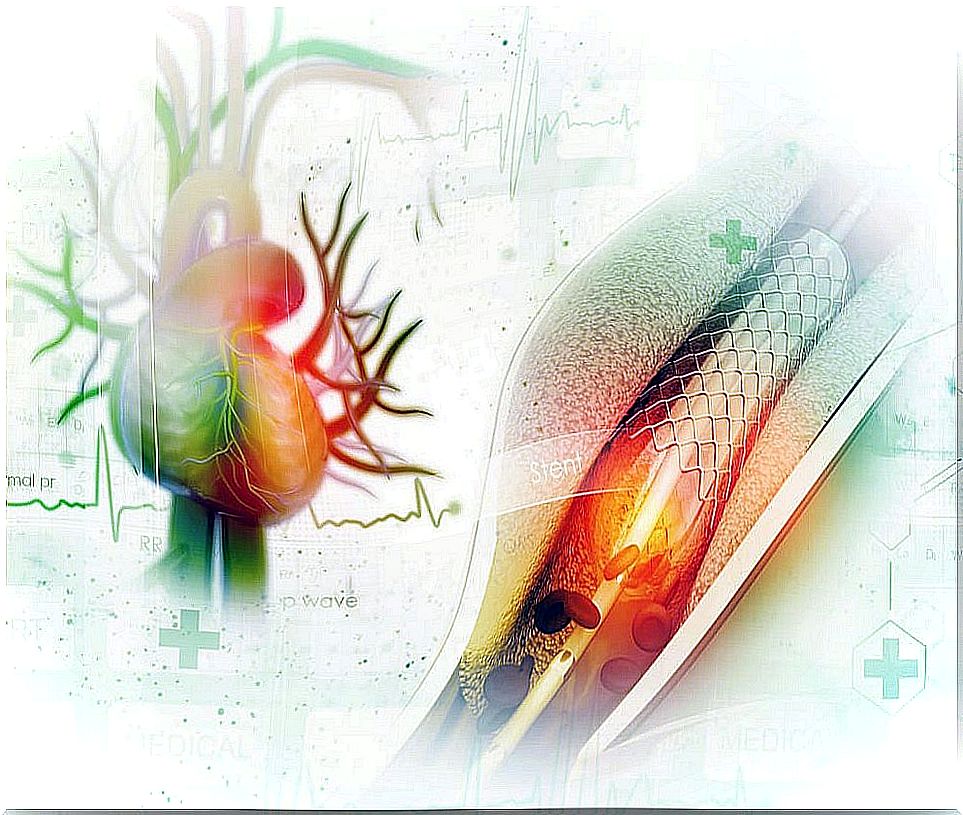
Coronary angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention . This is a procedure to unblock the blood vessels that carry blood to the heart.
The blood vessels, called coronary arteries, retain fatty material that, by preventing proper circulation, reduces the amount of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle.
With coronary angioplasty , a small inflatable balloon is temporarily inserted in the area of the obstructed artery, which later, when inflated, compresses the obstruction to expand it.
What is coronary angioplasty?
Coronary angioplasty is a procedure performed under local anesthesia in a hemodynamic room.
Before starting the intervention, analgesics and anticoagulants are administered, in order to avoid the formation of a blood clot. Later, the area where the catheter is inserted is shaved, and then the doctor makes a small surgical incision in the artery to insert it.
The catheter is often placed in the arm or wrist, or in the upper leg (groin). Once positioned, the physician guides the balloon catheter into the blocked artery, supported by live X-ray images.
A dye is also injected into the body to enhance blood flow through the arteries. In this way, it is possible to identify any blockage in the blood vessels.
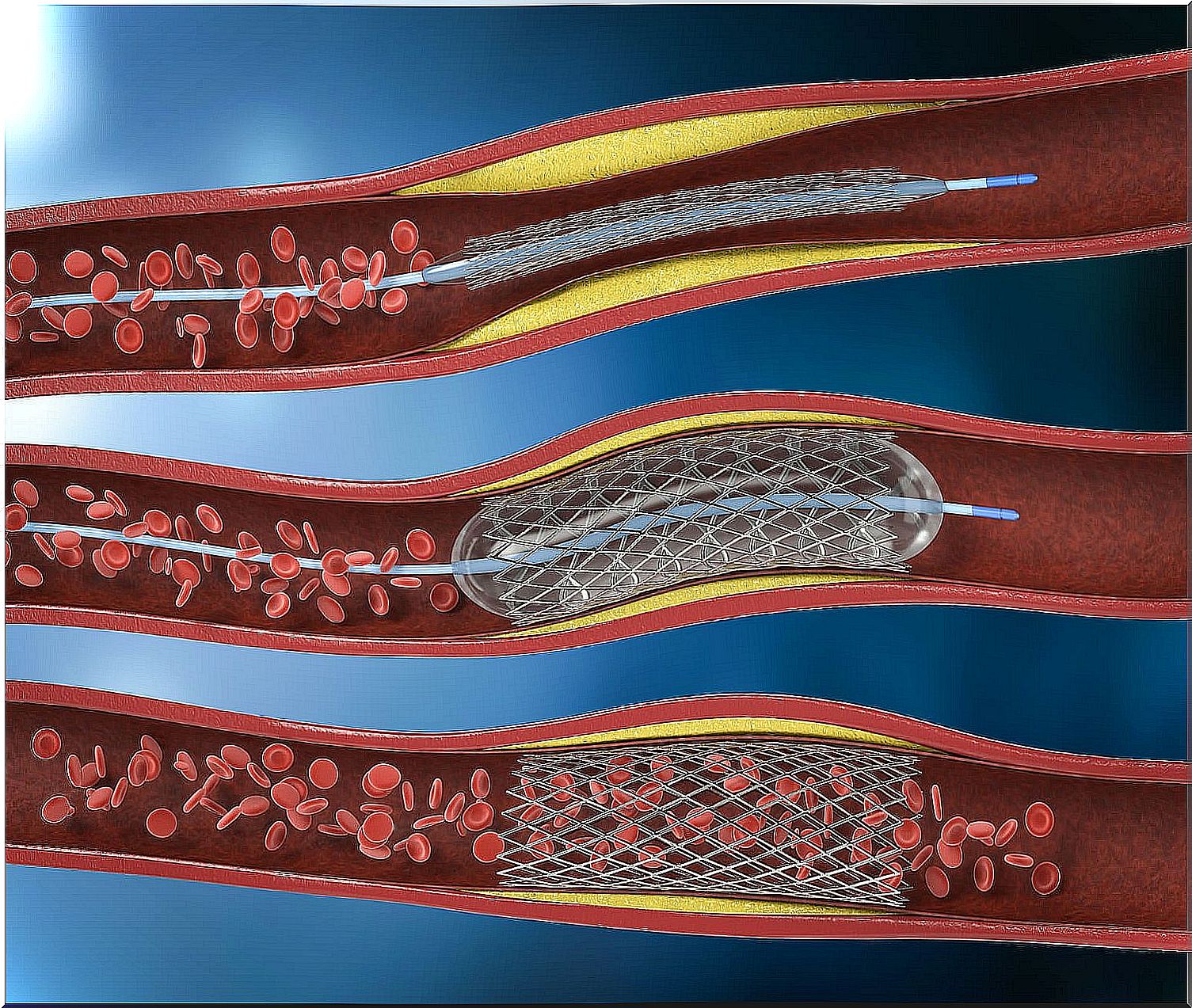
After locating the correct site with the catheter, the balloon is inflated to compress the plaque against the walls of the artery. This is the procedure that allows to restore the blood flow that circulates inside it towards the heart.
Then, in most cases, a small metal mesh tube known as a stent is implanted . After being located in the place where the obstruction was, it expands and remains attached to keep the artery open.
The stent may be coated with drugs to help keep the artery open ( drug- eluting stent ), although these are only used in some people.
After the procedure, a compression bandage is placed and the patient is hospitalized in a coronary care unit to receive continuous controls. Depending on the evolution, discharge can be the same day, after 24 hours, or in 48 hours.
When is this procedure used?
Angioplasty is used to treat a type of heart disease known as atherosclerosis. In this, the arteries are narrowed or blocked by the accumulation of fatty and cholesterol plaques.
Your doctor may suggest intervention when medications and lifestyle changes are not enough to improve heart health. In general, angioplasty is used in cases of:
- Blockage in a coronary artery during or after a heart attack.
- Blockage or narrowing of one or more coronary arteries that interferes with the functioning of the heart. (heart failure)
- Narrows that interfere with circulation and cause persistent chest pain (angina).
Angioplasty is not for everyone. If there are multiple blockages, if their location is in certain places, or if the heart muscle is weak, coronary bypass surgery may be a better option.
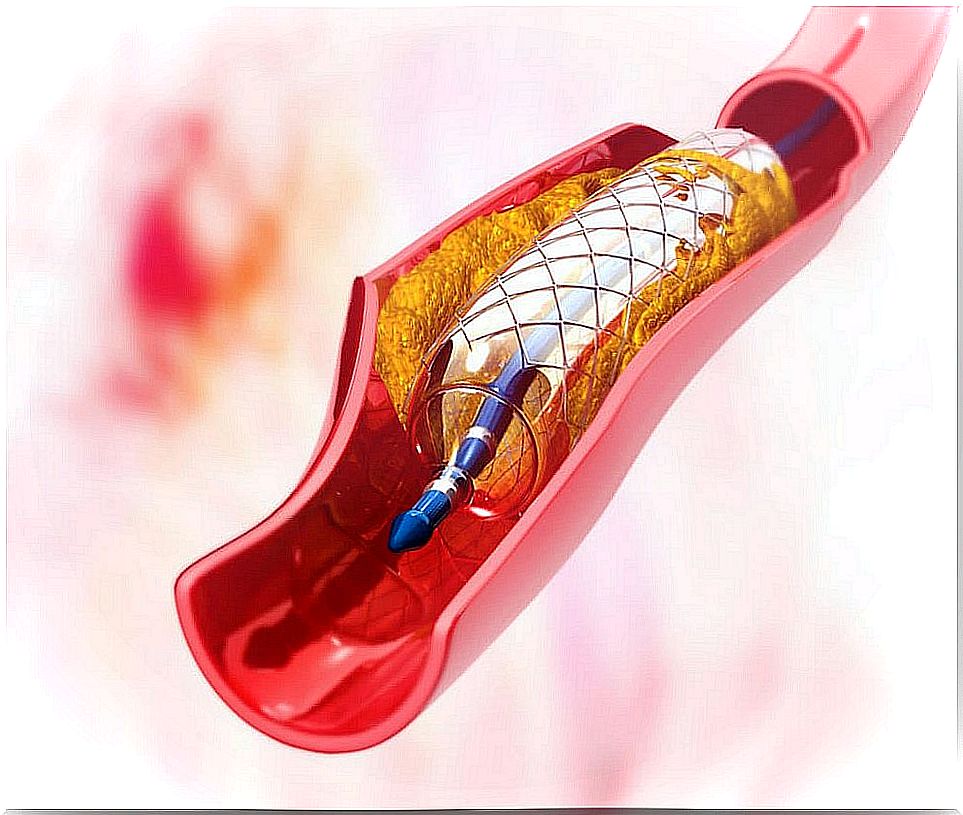
Risks
This intervention is safe. However, in small cases some complications may occur . For this reason, the doctor always performs a medical evaluation of the patient to discuss a treatment according to their needs.
Some of the risks of angioplasty and stent placement include:
- Heart attack.
- Cardiac arrhythmias.
- Stroke (rare).
- Formation of blood clots
- Coagulation of the interior of the stent .
- Damage to a valve or blood vessel.
- Bleeding or clotting in the area where the catheter was inserted.
- Kidney failure (more common in patients who also have kidney problems).
- Allergic reaction to the drug used in the drug- eluting stent , the stent material, or the radiographic contrast medium.
Previous recommendations
Before carrying out the coronary angioplasty procedure, it is vitally important to follow some recommendations:
- Tell your doctor if you have allergies to shellfish or if you have had a bad reaction to contrast material or iodine.
- Tell your doctor if you are taking prescription, over-the-counter, or herbal remedies.
- Prescription drugs before the exam should be taken with only a small sip of water.
- Do not eat or drink anything for 6 or 8 hours before the intervention.
Expectations
After coronary angioplasty, most patients have a marked improvement in circulation through the coronary artery and heart. This can help avoid more complex procedures such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
However, it is important to consider that it does not act as a cure for the cause of the blocked arteries. Therefore, new constrictions or obstructions may occur in the future.
Improving eating habits, getting regular exercise and avoiding tobacco are essential to reduce the chances of having another blocked artery.